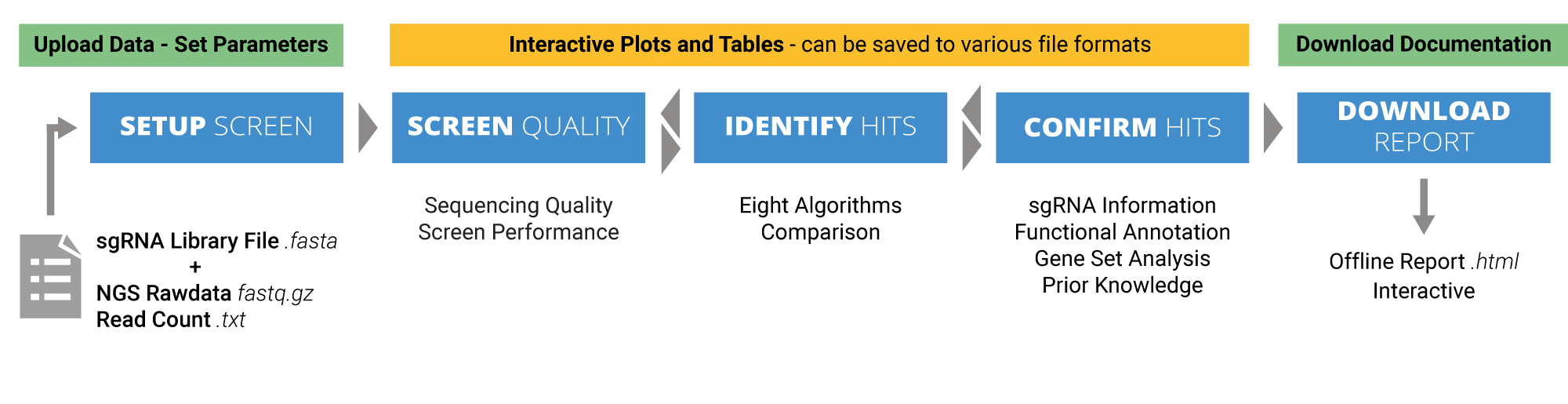
CRISPR-AnalyzeR.org offers you a web-based analysis plattform for your pooled CRISPR Screens.
Last Update: 2018-01-16 Version 1.50
CRISPRAnalyzeR is a user-friendly analysis suite for pooled CRISPR/Cas9 screens
Explore your Data, Explore your Analysis.
CRISPRAnalyzeR is a web-based analysis platform for pooled CRISPR screens. CRISPRAnalyzeR was developed with user experience in mind and provides you with a one-in-all data analysis workflow. And once you are finished, you can download all the data as well as your analysis as an interactive HTML report.
CRISPRAnalyzeR offers the following features
- Interactive
- FASTQ/NGS Quality
- Easy-to-use
- Screening Quality
- 8 different Hit-Calling methods
- Gene Annotation
- In-depth information about Genes and sgRNAs from 26 external data ressources
- Essential Genes
- Gene Ontology
- KEGG Analysis
- Protein Interactions
- Gene Set Analysis
- Fully-interactive offline Report
Download CRISPRAnalyzeR for offline use
You can use our online web service, but also download CRISPRAnalyzeR to install it on your local computer or within your lab/institute. CRISPRAnalyzeR is open-source and free for non-commercial use, please check out the download pages below.
CRISPRAnalyzeR can be downloaded so you can install it on your computer
For further information please check our Github page:
Or download CRISPRAnalyzeR directly:
Data Upload Upload your FASTQ Screening Files and sgRNA Library
As a first step, you need to upload your sequencing files and your sgRNA library file
- both are required for the data analysis.
Sequencing files can either be
read count files (
.txt - please check the format) or zipped FASTQ files (
.fastq.gz).
Sample Data
In case you like to try out CRISPRAnalyzeR without your own data, we have some sample data ready for you. All you need to do is download one of the sample data files, extract them - everything you need is included. Each data package consists of a sgRNA library file (.fasta) and NGS rawd ata (.fastq.gz) or read count files (.txt).
Focused Screen (12000 sgRNAs, custom library)
This 12k custom sgRNA library was published before in
F. Heigwer*, T. Zhan*, M. Breinig, J. Winter, D. Brügemann, S. Leible, M. Boutros,
CRISPR library designer (CLD): software for multispecies design of single guide RNA libraries,
Genome Biol., 2016, DOI:10.1186/s13059-016-0915-2
Sample Data with Read Count Files
In this package you will find 4 readcount files and a sgRNA library FASTA file.
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PBS-Replicate1.txt | Read Count file for untreated replicate 1 |
| PBS-Replicate2.txt | Read Count file for untreated replicate 2 |
| TRAIL-Replicate1.txt | Read Count file for TRAIL-treated replicate 1 |
| TRAIL-Replicate2.txt | Read Count file for TRAIL-treated replicate 2 |
| pilotscreen.fasta | sgRNA library FASTA file with 12000 sgRNAs |
Sample Data with NGS FASTQ.gz Files
In this package you will find 4 .fastq.gz NGS files and a sgRNA library FASTA file.
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PBS-Replicate1.fastq.gz | NGS FASTQ.gz file for untreated replicate 1 |
| PBS-Replicate2.fastq.gz | NGS FASTQ.gz file for untreated replicate 2 |
| TRAIL-Replicate1.fastq.gz | NGS FASTQ.gz file for TRAIL-treated replicate 1 |
| TRAIL-Replicate2.fastq.gz | NGS FASTQ.gz file for TRAIL-treated replicate 2 |
| pilotscreen.fasta | sgRNA library fasta file with 12000 sgRNAs |
Whole Genome Essential Genes Screen (90000 sgRNAs, TKOv1 library)
This screening data was published in
Steinhart,Z. et al. (2016)
Genome-wide CRISPR screens reveal a Wnt-FZD5 signaling circuit as a druggable vulnerability of RNF43-mutant pancreatic tumors.
Nat. Med.
Sample Data with Read Count Files
In this package you will find 3 read count files and a sgRNA library fasta file.
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| TKO_readcount_initial1 | Read Count file for Day 0 |
| TKO_readcount_final1 | Read Count file after 20 cell doublings (replicate 1) |
| TKO_readcount_final2 | Read Count file after 20 cell doublings (replicate 2) |
| FASTA_TKO_90K_library.fasta | sgRNA library FASTA file for this screen with 90000 sgRNAs |
Data Upload
You can upload NGS FASTQ.gz sequencing data or Read Count Files (.txt) in addition to your sgRNA library file (.fasta).
sgRNA Library File in FASTA format
The sgRNA library file must be provided in a FASTA format. This library file is not only used to identify the genes to which your sgRNAs belong but also allows CRISPRAnalyzeR to annotate your screen correctly.
Example files for the most common sgRNA libraries can be downloaded from below at the end of the help section.
>ENSG00000006042_0_4299.561 GGAGCCCTCTGAGTTAGAAC
Sequencing Data (NGS .FASTQ files)
Your screening data can be uploaded either as gzipped NGS FASTQ (.fastq.gz) or tab-separated Readcount(.txt) files. In case you upload FASTQ files, CRISPRAnalyzeR uses bowtie2 to map the FASTQ reads against the provided sgRNA library file. More advanced users can adjust bowtie2 parameters in the FASTQ Options Box at Step 3. Since FASTQ files are large, we would ask you only upload gzip-compressed files as they are usually provided by your sequencing machine. In this case, the files should end with .fastq.gz. Otherwise, please compress them using gzip first.
Tab-Separated Read Count Files
You can upload tab-separated read count files, in which every line contains a unique sgRNA identifier as well as the number of reads assigned to it. Please note that the sgRNA identifiers must be the same as in the sgRNA library file you provide. Since CRISPRAnalyzeR performes the the normalization, you can upload raw read count files.
Example of a tab-separated read count file:
sgRNA Count AAK1_104_0 0 AAK1_105_0 597 AAK1_106_0 145 AAK1_107_0 0 AAK1_108_0 0 AAK1_109_0 142
Extraction of your uploaded FASTQ.gz files
In case you upload FASTQ files instead of Read count files, your FASTQ data is extracted before the identification of your single sgRNA reads. For this purpose, CRISPRAnalyzeR needs to know how your FASTQ files do look like and how it can identify the barcode of each single sgRNA. By default, this barcode is the 20 nt target sequence as it is defined in the sgRNA library file you uploaded. To extract this information from your sequencing data, CRISPRAnalyzeR requires a so-called regular expression.
For your convenience, CRISPRAnalyzeR already provides you with pre-defined settings for the most common libraries and vector systems. As an alternative for more advanced users, you can also type in your own regular expression.
Pre-Made sgRNA library files for download
CRISPRAnalyzeR offers you pre-made sgRNA library fasta files for commonly used CRISPR libraries.
Please email us if you want your sgRNA library file to be distributed with CRISPRAnalyzeR.
| Library Name | Lab | Pubmed ID | Addgene | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLD Benchmarking | Boutros | 27013184 | NA | FASTA |
| Gecko V2 | Zhang | 25075903 | A+B FASTA A only FASTA B only FASTA | |
| Gecko V2 MOUSE | Zhang | 25075903 | A only FASTA B only FASTA | |
| Torronto KnockOut Library (TKO) | Moffat | 26627737 | 90K FASTA 85K FASTA | |
| Brunello | Doench | 26780180 | FASTA | |
| CRISPRa / CRISPRi | Weissmann | 25307932 | not available yet | |
| Human Lentiviral sgRNA library high cleavage activity | Sabatini | 26472758 | 185K FASTA | |
| Human Lentiviral sgRNA sub libraries | Sabatini | 24336569 | not available yet |
sgRNA Library - How To
sgRNA library files must be in FASTA format and include a unique sgRNA identifier as well as the guide target sequence (typically 19-21 nt) in 5'->3' direction.
An example of a FASTA file structure
>ENSG00000006042_0_4299.561 GGAGCCCTCTGAGTTAGAAC >ENSG00000006042_5_4299.588 GAAGATGCCTCGTAAGGCCA >ENSG00000006042_6_4299.588 GAGATGCCTCGTAAGGCCAT
sgRNA library file structure
A single item within the FASTA file consists of two lines. In this case it is the the sgRNA identifier with its target sequence. The first line is used to identify the item. It always starts with a > followed by the sgRNA identifier. The second line provides the corresponding sgRNA target sequence without the PAM sequence .
How to select the correct Regular Expressions for sgRNA libraries
Regular Expressions are used to extract the gene identifier from your sgRNA identifier. This is important as we want to provide you not only a gene-based analysis, but also additional visualizations and information about your candidate gene. To find a matching regular expression, you need to know the structure of such an expression and of course, the structure of your sgRNA identifier as it is used within your library file. Regular expressions for our pre-made libraries can be found below .
CRISPRAnalyzeR provides you with pre-defined regular expressions for commonly used vector systems. Alternatively, see below how to find the correct expression for your custom library.
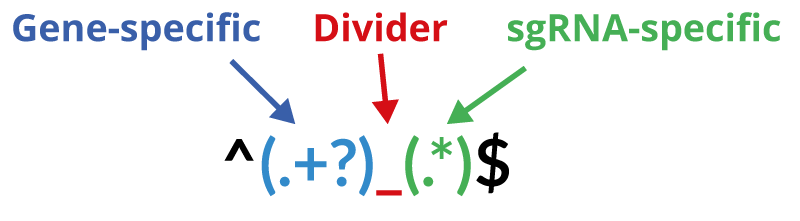

How to find the right Regular Expression
A Regular Expression is used to detect both the gene and sgRNA identifier for each sgRNA within your library file.
Note the brackets which are necessary. Regular Expression for the pre-made library FASTA files are provided below.
NGS Sequencing Files (.fastq.gz)
You can also provide raw data NGS files directly from your sequencing machine in a FASTQ format. Since FASTQ data can be large, the files which must be compressed using GZIP (.fastq.gz file ending). CRISPRAnalyzeR extracts all information from your FASTQ NGS file and performs the mapping against the sgRNA library file. Please make sure the FASTQ extraction pattern in Step3 matches the vector system you used for screening.
Example of a FASTQ file
@M01100:63:000000000-AMJC7:1:1101:21768:1401 1:N:0:1 TTGGATTCTTGTGGAAAGGACGAAACACCGTTCCCTGCAGCCCTCATGCGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAAT + CCCCCGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGFGGGGGGGGGGGGGGFGFDGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGPlease provide FASTQ files in a gzipped format (.fastq.gz)
CRISPRAnalyzeR needs to know which plasmid you used
In order to find the sgRNA target sequence (which is used as a barcode to identify the sgRNA), CRISPRAnalyzeR needs to know where to find it within your sequencing data.
For this purpose, regular expressions are used to extract this information
from your sequencing rawdata.
You can have a look at the plasmid map of the vector you used and try
to identify the left and right flanking sequences next to the sgRNA target
sequence (as illustrated below).
Alternatively you can use one of the pre-defined settings depending on your
vector system.
You can find the required regular expression for your screening vector the following way

Regular Expressions are used to extract the sgRNA target sequence barcode from your NGS FASTQ file.
To find a matching regular expression, you need to know the sequence or
name of the vector you used for performing the lentiviral transduction.
All you need to do is select a couple of bases flanking your sgRNA target
sequence on the left and right side.
CRISPRAnalyzeR provides with pre-defined settings for the most common screening systems (see below), but you can use your custom system as well.
In this case, select CUSTOM in Step3 and enter a custom regular expression by the addition of
2-4 bases of both the left and right flanking sequences on the left and
right site of the bracket. For the above shown example you could use the following regular expression for a sgRNA target sequence of either 20 or 21 nt in length:
The expression to detect the sgRNA target sequence is shown in blue color. Don't hesitate to ask us for help. CACC (.{20,21}) GTTTT
You can modify the pre-defined settings or add your own custom regular expression
Just tick the checkbox and enter a custom regular expression.
You can use the pre-defined settings for the most common screening vectors:
| Plasmid Name | Lab | Addgene ID | Expression required for Step3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lenticrisp V2 | Zhang | 52961 |
Default Setting
ACC(.{20,21})G
|
| Lentiguide (Puro) | Zhang | 52963 |
Default Setting
ACC(.{20,21})G
|
| Human Lentivirus Library V1 | Haoquan Wu | 69763 |
GTTT(.{20})GT
|
| pLCKO (TKO Library) | Moffat | 73311 |
ACCG(.{20,21})G
|
| pU6-sgRNA EF1Alpha-puro-T2A-BFP (CRISPRa/i) | Weissman | 60955, 62217, 60956 |
Default Setting
GTTG(.{20})G
|
Step 1: Please select the screening library
Please select which screening library you would like to analyze
But you can always analyze any type of pooled CRISPR screen by selecting CUSTOM
Step 1a: Upload Your sgRNA Library File
You can download pre-made sgRNA library FASTA files from the help section.
The regular expression depends on how you designed the sgRNA identifiers within your sgRNA library file.
For more information please see the help where you can also download pre-made FASTA library files.
Some Examples:
An example from your sgRNA library
This is how CRISPRAnalyzeR detects the gene from your sgRNA identifier.
Please select the regular expression from the left dropdown menu or type in your own. You selected the correct regular expression in the case your gene is highlighted in blue colour.Expert Options
You can add/modify the regular expression
Do you want to use a custom regular expression for the FASTA library?This will override the default settings to the left and is only for expert users.
Please check out the help or the tutorials section to find further information.Optimize sgRNA Library File
By default, CRISPRAnalyzeR optimizes and performs consistency checks. If you have problems, you can disable the optimization procedure.Step 2: Upload Your Sequencing Files
New to CRISPRAnalyzeR? Try our sample data:
The sample data can be used with the default settings.
You can upload the following files:
- Read Count Files (.txt)
- Already mapped read count files in .txt tab-separated format
- NGS Sequencing Files (.fastq.gz)
- Compressed FASTQ files as they are provided by the sequencer.
Rename Files
Example of a read count file (.txt)
The sgRNA identifier needs to be TAB-separated from the counts.
sgRNA Count ENSG00000053900_GAAAGCAATGAGATCCCGCT 28 ENSG00000053900_GAAGCAATGAGATCCCGCTT 62 ENSG00000053900_GAAGCGGGATCTCATTGCTT 92
Example of a FASTQ file (not compressed)
The file needs be GZIP-compressed.
@M01100:47:000000000-AH40C:1:1101:12289:2057 1:N:0:4 AACACCGTCAGTGTGCTTGCCCCACTGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTT + GGGGGGGGGGDGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG @M01100:47:000000000-AH40C:1:1101:8758:2058 1:N:0:4 AAACACCGGTTTTGAAACTGCGGACACGTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTA + GGGGGGGEGGGGGGGGGDGGFGGGEEGGFFGGFFCFFF=AFF<CEFFF@EFE
Step 3: Set FASTQ Options (if FASTQ files uploaded)
Expert Options
You can modify / add your own regular expression
Do you want to use a custom regular expression?
This will override the default settings to the left and is only for expert users.
Please check out the help or the tutorials section to find further information.You can override the warning for low alignment rates
By default, CRISPRAnalyzeR prevents you from data analysis in case the alignment rate is below 30%. However you can override this to also use samples of such low quality.This is only for expert users.
Do you really want to override the alignment quality check?Create a FASTQ data quality report
By default, CRISPRAnalyzeR generates a FASTQ data quality report, which can take some time. However, you can turn it off in case you are in a hurry.Perform FASTQ extraction in fast mode
By default, CRISPRAnalyzeR processes FASTQ files using a specialized tool for faster processing. In case you have issues with FASTQ extraction (e.g. all read counts are 0), you can try to disable the fast processing of FASTQ files and revert back to the old method.Data Review Review your Data and Download Rawdata Files
Review your uploaded data and download generated read count files or the quality report of your FASTQ files.
How can I download read count files?
You can download all read count files CRISPRAnalyzeR created for you.
CRISPRAnalyzeR gives you the opportunity to download the read count files for your samples.
In case you uploaded FASTQ.gz data, the read count files have been generated by mapping your sequencing data against your sgRNA library. If you come back to CRISPRAnalyzeR, you can then just upload the read count files together with your sgRNA library file, which is much faster.
The read count files are tab-separated text files and come within a gzip archive.

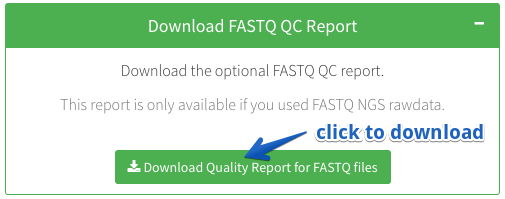
How can I download a quality report for my FASTQ.gz sequencing data?
CRISPRAnalyzeR also provides an extensive quality report for your sequencing data.
Once you upload FASTQ.gz sequencing data, CRISPRAnalyzeR will create a sequencing data quality report. The report is generated using the Rqc package
Welliton Souza and Benilton Carvalho (2016). Rqc: Quality Control Tool for High-Throughput Sequencing Data. R package version 1.6.2. https://github.com/labbcb/Rqc
What information is provided in the overview table?

| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Original Filename | The name of the uploaded file |
| Provided Nameame | The name you provided after uploading the files |
| Type | Either Fastq for sequencing files or Readcount for read count data |
| Size | The filesize |
| sgRNA Extraction Ratio | The ratio gives an estimate of how many sequencing reads were extracted according to the selected regular expression. In general this should be higher than 80%. |
| Reads Mapped To Reference | CRISPRAnalyzeR maps your raw data sequencing files to your sgRNA library file and tells you, how many reads were mapped to your sgRNA library. Each sequencing read can be mapped only once (Aligned once), multiple times or it might be that a read cannot be mapped to your library at all. |
| Reads passed Quality Threshold | You select a quality threshold for the mapping of sequencing reads to the sgRNA library. This is the percentage of reads which have passed the selected quality criteria. |
| Reads Used in Total | This is the percentage of reads that is finally used for the data analysis after the sequencing data handling, which includes the extraction of sgRNA sequences, the mapping to the sgRNA library and the applied mapping quality threshold. |
Download Read Count Files
For your convenience, just get the generated read count files.
Read count files can be used the next time - which is much faster than using FASTQ data.Download Readcount files
Download FASTQ QC Report
Download the optional FASTQ QC report.
This report is only available in case you uploaded NGS raw data.Download Quality Report for FASTQ files
Overview of Uploaded Data and Samples
Download Analysis Data
Download All Analysis Data
You can download all raw data form the individual hit calling methods either as a tab-separated .TSV file or as a fully formatted .XLSX Excel file. Download .TSV Download as Excel .XLSXDownload All Intermediate Analysis Data
Download .ZIPDownload All Generated Raw Data
This will download everything that has been generated and is only for advanced users. The filesize can be larger than 1 GB. Download .ZIPDownload the sgRNA Re-Evaluation File
You can download the sgRNA Re-Evaluation file that includes genomic locations and scores for each individual sgRNA of your library. Download .TSVSetup Define treatment groups and gene identifier
Tell CRISPRAnalyzeR which treatment groups you have, assign samples to it and adjust the gene annotation parameters.
In order to assign samples to a group, the upload of your samples needs to be completed.
You did a mistake? Don't worry, you can easily change the setup by
clicking on the Change Setup button.
Why do I need to set groups?
CRISPRAnalyzeR performs hit analysis by comparing two groups, whith each group containing the corresponding samples.
All hit analysis methods that are implemented in CRISPRAnalyzeR require the use of two groups that are compared. This means, you need to assign each sample to either one of the groups you would like to compare. As an example, this could be a Day0 vs a Day12 group or a Control vs a Drug Treatment group.
How can I setup my treatment groups?
CRISPRAnalyzeR will always compare two treatment groups
You can increase the number of groups, but the minimum required number is 2. If you like you can also name each group.
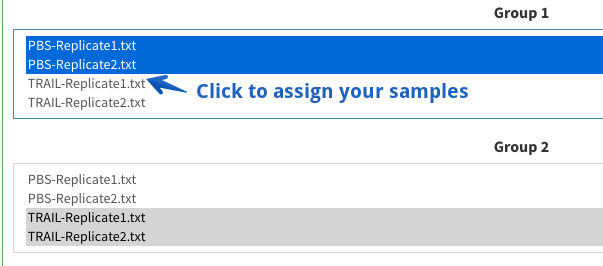
How can I assign my samples to the groups?
You can assign each file to one group by clicking on the sample name. If you like to have more than one file per group, keep the CMD or CTRL button pushed while selecting the samples. Please note that your are not allowed to use the same sample in more than one treatment group.
Why do I need to set gene identifiers?
CRISPRAnalyzeR needs to know the type of gene identifier used for the screen - and can automatically convert it for you
CRISPRAnalyzeR needs to know in which organism your screen was performed and which gene identifier is used in the sgRNA library file. With this information, CRISPRAnalyzeR can offer you extensive gene annotation and visualizations.
CRISPRAnalyzeR expects the type of organism, the gene identifier and which identifier you would like to convert it to.
If you do not want to convert your gene identifier, please select the same identifer twice.Supported Gene Identifiers
| Gene Identifier | Example |
|---|---|
| Ensembl Gene ID | e.g. ENSG00000141510 |
| EntrezGene ID (also NCBI Gene ID) | e.g. 7157 |
| HGNC ID | e.g. 11998 |
| HGNC symbol | e.g. TP53 |
| Unigene ID | e.g. 7157 |
| Uniprot Gene Name | e.g. TP53 |
Step 1: Which treatment groups do you have?
Step 2: Assign your files to the groups
One sample can only belong to one treatment group, you are not allowed to assign two different groups to the same sample.
We strongly advise you to have replicates, however you can still run the analysis even with a single sample per group.
Please note: Analysing data without at least two replicates per sample is not advised since most analysis methods do not work properly without replicates.
You can select mutliple samples by pressing CMD or CTRL
Step 3: Adjust the gene annotation parameters
If you want to stay with your gene identifier, just select the same identifier twice. Please note: Gene ID conversion is done using the Ensembl BiomaRt service.
Settings Analysis Settings
In the settings tab all important parameters for the Hit Analysis are
set.
Moreover you can define control genes and select which of the groups you
defined are compared.
All information from the Data Upload and Setup page remain unaffected.
How do I setup screening controls?
You can set positive and non-targeting controls which will help you to judge your screen performance
What are positive controls?
Positive controls are genes, for which the screening outcome is known. These will tell you whether your screening setup worked and are very important to judge your screening performance.
Which gene can be used as a positive controls strongly depends on the type of screen. For Viability/Dropout screen, essential genes can be used as positive control.
What are non-targeting contols?
Non-targeting controls are articicial genes, which are not present in the screened organism. Since these controls don't have any target in the screening organism, they can be used to judge the screening variability. Common non-targeting controls are GFP or random sgRNA sequences.
Adjust thresholds used for hit identification
CRISPRAnalyzeR uses different algorithms to analyze your data
For each algorithm, you can set a p-value threshold that is used to discriminate between significant and non-significant hit candidates.
- Wilcox
- Analysis on sgRNA read count Wilcoxon analysis is based on a Mann-Whitney test between a random/non-targeting sgRNA set and all sgRNAs for each targeted gene. If no non-targeting controls have been set, randomly picked sgRNAs are used as test reference instead.
- DESeq2
- Analysis on Gene read count For this analysis, the DESeq2 package is employed on gene-level read count to find potential hit candidates between the treatment groups.
- MAGeCK
- Analysis on sgRNA read count MAGeCK analysis is performed on sgRNA readcount comparing the selected treatment groups. For this, MAGeCK is implemented as described on the MAGeCK website
- edgeR
- Analysis on sgRNA read count EdgeR hit analysis is performed on sgRNA read counts followed by a gene enrichment analysis. EdgeR has been implemented as described here Dai et al. (2014) edgeR: a versatile tool for the analysis of shRNA-seq and CRISPR-Cas9 genetic screens, F1000Research, 3:95.
- sgRSEA
- Analysis on sgRNA read count SgRSEA (single-guide RNA Set Enrichment Analysis) has been implemented as described in the corresponding R package available at CRAN
Can I remove low / high read counts from the analysis?
If you like to remove sgRNAs with low or even high read counts from your analysis, just activate the checkbox and tell CRISPRAnalyzeR the desired threshold. Each sgRNA having a read count below/above or equal to the threshold will be removed from the analysis.

How can I analyze two groups?
CRISPRAnalyzeR will run the analysis between two groups
You can select the two groups out of all groups you have defined on the Set Groups And Identifier page.
Can I run multiple analysises?
CRISPRAnalyzeR always runs a pairwise analysis between two groups. If you want to compare additional groups, you can always come back to the Set Analysis page and click on the Change Setting button at the bottom. This allows you to change all analysis parameters and start a new analysis without uploading the data again.

Step 1: Set Controls (optional)
Step 2: Adjust Hit Calling Thresholds
Differential Hit Analysis
CRISPRAnalyzeR supports 6 different analysis methods which will be used to analyse your screen. Please define the p-value cutoffs for each individual analysis. From our experience, the p-value threshold for DESeq2 should be set very low.Wilcox
DESeq2
MAGeCK
sgRSEA
EdgeR
BAGEL
Essential Genes Analysis
You can define the range in which you expect the BAGEL cutoff.ScreenBEAM
Do you want to run ScreenBEAM data analysis? This will increase the analysis calculation time by at least three times.
Step 3: Select which Groups to Compare
Step 4: Removing low/high Read Counts from Analysis
For a more robust analysis, we recommend to remove sgRNAs with a read count of less than 20.
Screen Quality FASTQ Sequencing Quality
In case you provided NGS Fastq files, you will find visualizations of the sequencing quality on this page.
What do the plots tell me?
CRISPRAnalyzeR provides you with a set of FASTQ quality plots once you uploaded FASTQ sequencing files
CRISPRAnalyzeR uses the Rqc Bioconductor package to provide you with FASTQ quality information.
http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/vignettes/Rqc/inst/doc/Rqc.html Souza W and Carvalho B (2016). Rqc: Quality Control Tool for High-Throughput Sequencing Data. R package version 1.8.0, https://github.com/labbcb/Rqc.
Cycle-sepcific quality plots
GC content
Shows the GC-base content for each sequencing cycle
Quality Distribution
Shows the quality score proportion per cycle. Colors are presented in a gradient Red-Blue, where red identifies calls of lower quality.
Average Quality
Describes the average quality score for each cycle of sequencing
Basecall Proportion
Describes the proportion of each nucleotide present at every cycle of sequencing.
Read Frequency and Width
Read Frequency
Shows the proportion and frequency of sequencing reads.
Read Width
Describes the length of reads within the sequencing file.
Screen Quality Basic Dataset Stats
In case you like numbers, this is the tab for you.
Here you can have a look at raw numbers of your screen and get a feeling
for the quality of the screen.
In all Screening Quality plots these numbers are used for generating the
plots.
Overview
- Mean
- The mean read count of all sgRNAs/Genes in the dataset
- Median
- The median read count of all sgRNAs/Genes in the dataset
- Min
- The minimum read count of all sgRNAs/Genes in the dataset
- Max
- The maximum read count of all sgRNAs/Genes in the dataset
- SD
- The calculated Standard Deviation of all sgRNA/Gene read count in the dataset
- Missing
- The number of sgRNAs/Genes which have a read count of 0. In case the uploaded sgRNA FASTA library contains more items than the screening data, these sgRNAs/Genes will reported as missing.
Readcounts
The Readcounts tab allows you to browse through your readcount data. You can also sort according to the different columns and search for specific genes or sgRNAs. On the left you can select whether you wish to browse readcounts per sgRNA or get a summed-up readcount per gene.
Distribution
Described the log2 read count distribution for all sgRNAs of each dataset.
Did you know?
You can zoom into the plot by keeping the left-mouse button pushed. Moreover, you can select/deselect any dataset by clicking on the dataset name below the plot.
Controls
If you have set either positive or non-targeting controls in the Set Analysis Parameter section, read statistics for these controls are shown.
Read Depth
Shows the read count of each gene divided by the number of sgRNAs that contributed to it. This is used to give you an idea of read count depth normalized to the number of sgRNAs. The Read Depth plot shows you how many reads fall onto every gene present in your dataset. Positive controls (if set) are highlighted in red, non-targeting control (if set) are highlighted in blue color.
Did you know?
You can zoom into this plot for a closer inspection.
Screen Quality Sequencing coverage
A gooed coverage is a key to successfull CRISPR screens. Here you can check whether all sgRNAs are still present in your samples. It shows you how many sgRNAs/Genes were not present in the screening data and how many sgRNAs per gene are present at all.
Missing sgRNAs/Genes
The missing sgRNA/Genes tab shows you how many sgRNAs/Genes were not present in the sequencing data compared to the uploaded sgRNA library file. This means the read count for this particular sgRNA or the sum of sgRNA read counts for a particular genes is 0. If a read count threshold has been applied, removed sgRNAs are NOT listed as missing.
- Missing Genes
- Number of Genes in which all sgRNAs were not present in the dataset compared to the provided sgRNA library.
- Missing sgRNAs
- Number of sgRNAs which revealed a read count of 0 in the dataset.
- % of missing non-targeting sgRNAs
- The percentage of sgRNAs, which belong to the non-targeting control, that were not present in the dataset.
- % of missing positive control sgRNAs
- The percentage of sgRNAs, which belong to the positive control, that were not present in the dataset.
Designs per Gene
Distribution of sgRNA presence for all genes in the dataset. In case all sgRNAs for all genes are present, you will expect only one bar.
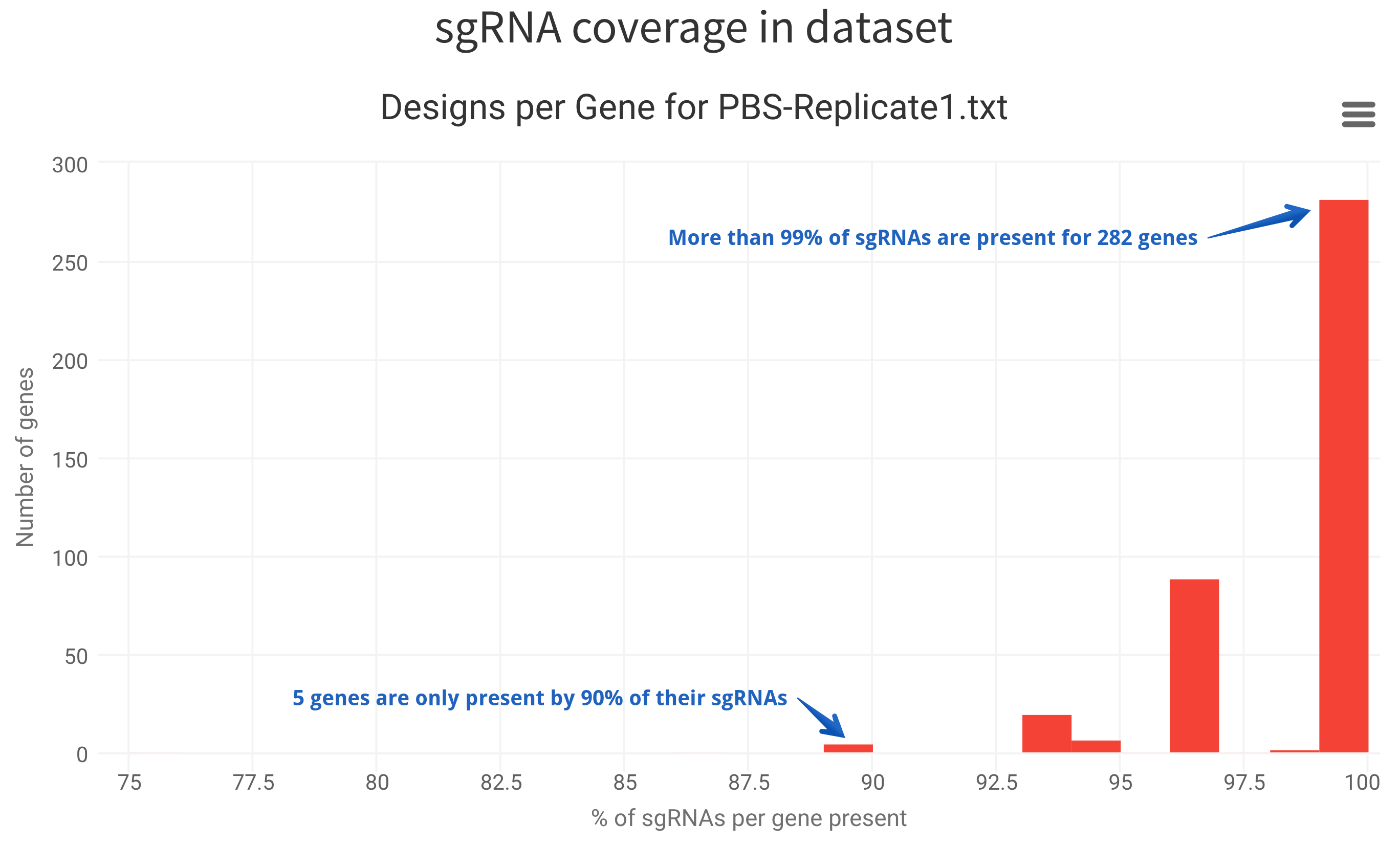
Screen Quality Sample comparison
For sure your screen was done in replicates. But how well are your replicates?
This page will give you the answer as an Overview, or more detailed incase you are patient.
Overview
A fast overview
Here you will find a boxplot visualization of the log2 Foldchanges or Z-Ratios between all uploaded samples on both gene and sgRNA level. This gives you a fast overview to check for outlying samples, that might have an unexpected influence on the analysis of your data.
Pairwise Comparisons
For a more detailed view
These plots allow you to directly compare two samples by both log2-Foldchange and Z-Ratio. With this you can inspect how foldchanges differ between your screning replicates.
Scatterplot Matrices
A fast overview
The grid gives you a fast overview of the correlation of your replicates. You can view the correlation for both sgRNA and Gene read count. CRISPRAnalyzeR calculates the Pearson as well as the Spearman coefficient. For a more detailed view, have a look at the compare datasets tab.
Scatterplots
For a more detailed view
If you are interested in a more detailed view, you can select two datasets or treatment groups and compare them on either gene or sgRNA level. You can highlight positive or non-targeting controls which will shown in red or blue color respectively. Moreover you can select multiple genes which will be highlighted in orange color within the scatterplot. For gene-based levels, please tick the 'Show the plot with gene level read count'. Moreover, you can get all scatter plots with log10-transformed data.
Screen Quality Principal Component Analysis
A principal component analysis can give you first idea how similar or differential your samples are and which of the samples you provided nicely group together.
What is Principal Component Analysis
A principal component analysis is a method to reduce multi-dimensional data into two-dimensional projection by keeping the information about the variance in the dataset. It tries to identify directions, for which the variation is maximum. These directions are called principal components.
Please check out the following article, in which PCA on genomic data is nicely explained. Nature Computational BiologyPrincipal Component Analysis
Screen Quality Heatmap Visualization
Large datasets can be visualized using a heatmap, which gives you an overview
of how your data looks like.
CRISPRAnalyzeR offers different heatmaps to visualize your data.
What Heatmap Visualizations can I use?
CRISPRAnalyzeR provides you different settings to adjust the heatmap visualization.
CRISPRAnalyzeR offers you six different types of heatmaps visualization. In addition, you can use K-Means clustering within selected heatmap types. Heatmaps allow you to look at your data in a structured way in order to check how your screen performed.
- Gene Abundance
- The gene abundance heatmap takes the read count of all sgRNAs for a given gene and calculates its fraction (in %) of the whole dataset.
- Gene Read Count
- With this type, the normalized read count for all sgRNAs of a given gene is summed up and visualized.
- Gene Top/Low
- Describes you how many sgRNAs for each gene where among the top or lowest 5 % of the dataset. This can be used to find potentially enriched or depleted genes.
- sgRNA Abundance
- The sgRNA abundance heatmap shows you the percentage of read counts wihtin the dataset accounted for each sgRNA.
- sgRNA Read Count
- This type describes the normalized read counts for each sgRNA in the dataset.
Did you know?
You can zoom into the heatmap to inspect interesting regions more closely. In addition, you can save an image of the current view using the upper right menu.
Step 1: Adjust the heatmap settings
You can adjust the heatmap using various parameters
You can download the plot via the upper right menu within the plot and add it to your CRISPRAnalyzeR Report by clicking on the Add Report button.
Please be patient while CRISPRAnalyzeR generates it for you.
Get your heatmap
Heatmap
Hit Calling Gene Ranking
CRISPRAnalyzeR performs data analysis using 8 different algorithms, which gives you a more sophisticated way to check for screening candidates. Take your time and have a look at each individual analysis method and compare them.
Which hit calling algorithms are implemented in CRISPRAnalyzeR?
CRISPRAnalyzeR offers you six different hit calling algorithm implementations to give you the chance to find the most robust hit within your screen. Since each algorithm performs the hit calling in a different way, we suggest you to have a look to all of them.
Before CRISPRAnalyzer applies hit calling, all data is normalized using DESeq2.
Wilcox
Analysis on sgRNA foldchangeThe Wilcox implementation is based on a two-sided Mann-Whitney-U test, which compares the sgRNA population foldchange (between your treatment groups) of each gene to either the population of the non-targeting control (if specified) or randomly picked sgRNAs. Finally a P-value correction according to Benjamini-Hochberg is applied to correct for multiple testing.
MAGeCK
Analysis on sgRNA read countsMAGeCK is a stand-alone algorithm to perform hit calling in pooled CRISPR screens. MAgeCK is based on a RRA ranking algorithm to identify hit candidates.
Li, et al. MAGeCK enables robust identification of essential genes from genome-scale CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screens. Genome Biology 15:554 (2014)
edgeR
Analysis on sgRNA read countsIn brief, all read count data is modelled using an overdispersed Poisson model. Gene dispersions are then estimated by conditional maximum likelihood and shrunk using an empirical Bayes procedure. Finally, differential expression is assessed using an adapted Fisher's exact test. EdgeR analysis has been implemented as previously published in
Dai,Z. et al. (2014) edgeR: a versatile tool for the analysis of shRNA-seq and CRISPR-Cas9 genetic screens. F1000Research, 3, 95.
DESeq2
Analysis on Gene-level read countsThe DESeq2 implementation is based on the DESeq2 R package. It uses the summed read counts of all sgRNAs for a given gene and tests for differential effects based on a negative binomial distribution model. In brief, eead counts for all sgRNAs are summed up to obtain the total read count per gene. DESeq2 analysis is performed on these read counts, which includes normalization, estimation of size-factors and variance stabilization using a parametric fit. A Wald test for difference in log2-foldchanges between both conditions is done to determine enrichment/depletion effects. For more information about DESeq2, please see the DESeq2 manual available at Bioconductor or the publication.
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S (2014). “Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2.” Genome Biology, 15, pp. 550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8.
sgRSEA
Analysis on sgRNA read countssgRSEA is based on the sgRSEA R package (Enrichment Analysis of CRISPR/Cas9 Knockout Screen Data), which is available at the R CRAN page. in brief, sgRSEA is based on a single-guide RNA Set Enrichment Analysis. First, sgRNAs are ranked by a signal-to-noise ratio. Then, the distribution of sgRNA ranks of a sgRNA set is compared with the overall distribution using a so-called enrichment score, which is based on a one-sided Kolmogorov Smirnov statistic and reflects the degree to which a sgRNA set is overrepresented at the top/the bottom of the ranked list.
Z-Ratio
Analysis on sgRNA/Gene-level read countsA Z-Ratio is calculated between your two treatment groups for each sample and was originally used for microarray data. The Z-Ratio has been implemented as previously published.
Analysis of Microarray Data Using Z Score Transformation Chris Cheadle, Marquis P. Vawter, William J. Freed, Kevin G. Becker J Mol Diagn. 2003 May; 5(2): 73–81. doi: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60455-2
What visualization does CRISPRAnalyzeR offer?
CRISPRAnalyzeR offers you three different visualizations for all hit calling methods that have been implemented.
- Ranked P-Values by significance
- Distribution of unadjusted P-Values
- Log2-transformed foldchanges plotted against the -log10 transformation of the corresponding adjusted p-values
CRISPRAnalyzeR performs the analysis to find more abundant (enriched) or less abundant (depleted) genes between your treatment groups. Genes which have shown a significant change, according to the p-value thresholds you have specified, are highlighted in red color in all plots.
Hit Calling Overview
This page gives you the overall view for each analysis method and allows
you to do a compare-on-a-glance.
Venn diagrams illustrate a hit candidate overlap for those that showed
up below the defined p-value threshold in the different algorithms.
How can I find overlapping hit candidates?
Select the analysis methods to see overlapping hit candidates
In case you select an analysis method using the check boxes below, CRISPRAnalyzeR includes its results to show overlapping hit candidates. Genes are only considered as overlapping candidates between the methods, if they are below the p-value threshold of each method that you have set in the analysis settings. If there are no overlapping genes, reduce the number of included analysis methods and check the individial hit calling candidates of each analysis method.
Gene List Table
You can select which analysis algorithms you would like to compare - and whether you would like to have a look at enriched or depleted hit candidates. Remember that enriched means the gene showed a positive fold change between your treated and untreated group, and depleted indicates the exact opposite (a negative fold change). You can select and de-select methods and by this, get the common hit candidates among them.
Venn Diagram
A Venn diagram provides you the information, how many genes overlap in the different analysis algorithms. The number within a shared area indicates the number of overlapping candidates between these methods. A detailed explanation on Venn diagrams can be found on Wikipedia.
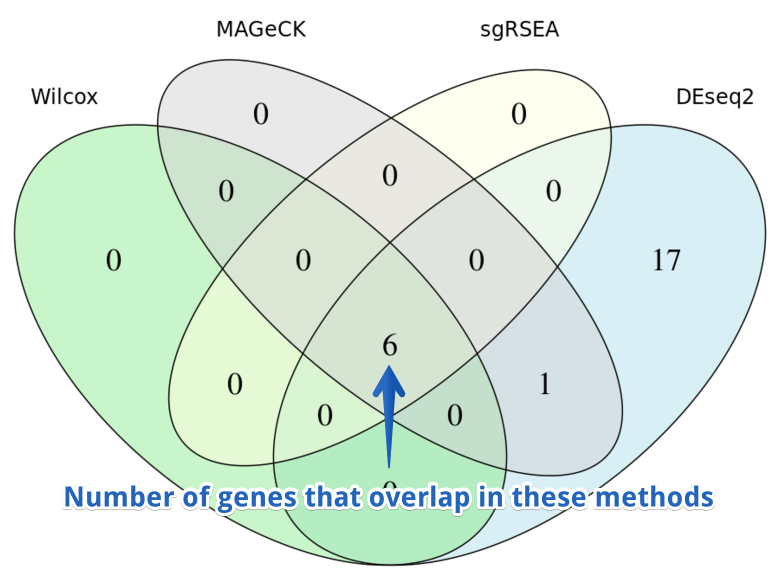
Find signficant candidates across all methods
Hit Calling Essential Genes
Compare your genes against the DAISY Core Essentials and known essential genes of various cell lines according to GenomeCRISPR.
DAISY Core Essentials
The DIASY core essential genes are derived from the publication by
Traver Hart et. al
Hart,T. et al. (2015) Systematic discovery and classification of human cell line essential genes Cold Spring Harbor Labs Journals.
GenomeCRISPR Cell Line Essentials
Hit Confirmation Gene Overview
The Hit Confirmation section will provide you with
more detailed information about your genes of interest.
This includes individual sgRNA performance, a genomic model,
predicted genome binding sites, predicted sgRNA scores as well as a brief overview
for each individual gene of your screen.
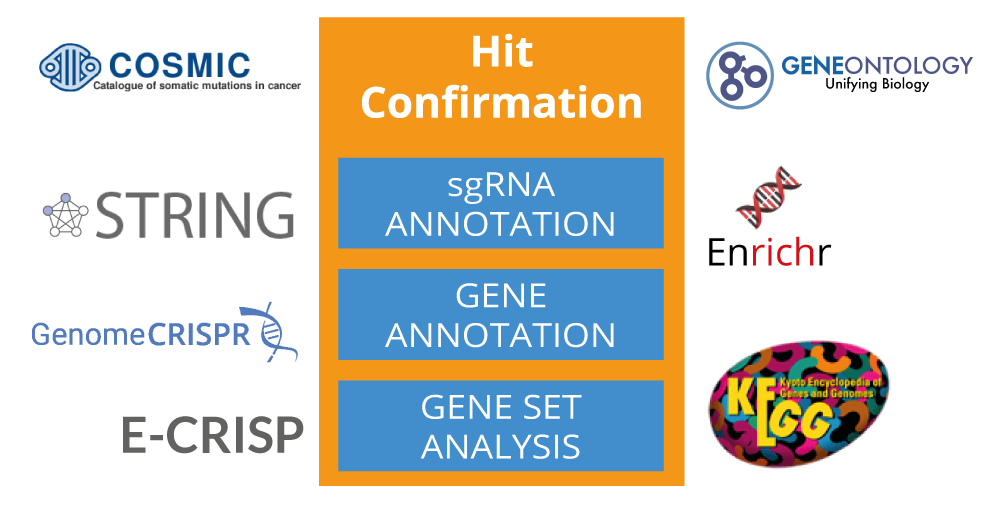
Once you select a gene, CRISPRAnalyzeR will gather all information for you
Why does CRISPRAnalyzeR reannotate sgRNAs?
CRISPRAnalyzeR reannotates every sgRNA within your screen using E-CRISP. With this information, CRISPRAnalyzeR can generate additional information and plots for, e.g. the genomic model or potential genomic binding sites.
Gene Information

General information about the selected gene are retrieved from Ensembl, EnrichR and KEGG.
Gene/sgRNA Model
CRISPRAnalyzeR creates a genomic view similar to a genome browser, which includes gene or sgRNA information.
Published Screens
You can check whether you gene of interest has been used in previously published CRISPR screens. Moreover, information about observed phenotypes is presented.
Gene Peformance
CRISPRAnalyzeR gives you a brief overview of how the selected gene performed in your screen compared to all other genes.
COSMIC Mutation Database

CRISPRAnalyzeR retrieves additional information about somatic cancer mutation from the Sange COSMIC database. Please visit the COSMIC website to find more information about the COSMIC database.
Gene Ontology
CRISPRAnalyzeR retrieves additional information from the the Gene Ontology Consortium. Please visit the Gene Ontology website to find more information about Gene Ontology.
Please select your gene of interest
After selecting a gene, CRISPRAnalyzeR will automatically start to retrieve all information.
Hit Confirmation sgRNA Performance
It is nice to know about possible hit candidates, but how about the sgRNAs that were used to target these genes?
On this page you can further investigate the performance and properties of sgRNAs targeting the select gene.
The sgRNA section of the In-Depth Analysis allows you to have a closer look the performance and properties of individual sgRNAs targeting the selected gene.
Readcount
After you have selected a gene on the left, you can check the read counts for each sgRNA targeting the selected gene. Moreover, you can select to get the normalized or non-normalized, raw read counts plotted. Remember that you can zoom into the plot as well as select/deselect the samples by clicking on their names in the legend below the plot.
Log2 Foldchange
This shows the fold changes of individual sgRNAs between your treatment groups in a log2-transformed visualization. You can sort the sgRNAs according to the log2 fold change.
Genomic Binding Sites
CRISPRAnalyzeR uses the re-evaluation feature of E-CRISP.org to reannotate your sgRNAs. This includes the analysis of predicted genomic binding sites, for which each sgRNAs is checked for potential genomic binding sites with a maximum of two mismatches and ignoring the first nucleotide base.
Z-Score
The Z-Score or standard score is a z-transformation according to this calculation.
Efficiency Scores
E-CRISP.org also provides some external efficiency scores. For more information, please visit the E-CRISP website.
- Seed GC %
- The GC content in per cent of the 8 basepairs proximal to the PAM sequence
- Doench
- Efficacy scoring as introduced by Doench et al. 2014 Nat. Biotech.
- XU
- Efficacy scoring as introduced by Xu et al. 2015 Gen.Res.
E-CRISP Scores
CRISPRAnalyzeR provides you with the scores that E-CRISP.org calculates for each sgRNA. An overview of the presented scores can be found at the E-CRISP website.
- Specificity
- Specificity Score
- Annotation
- Annotation Score
- Efficiency
- E-CRISP Efficacy Score
- CDS
- Coding Sequence Score
- Exon
- Exon Targeting Score
sgRNA Sequence
Here you can find an overview of your sgRNA target sequences, the fold changes, the Z-Score and the number of predicted targets for each sgRNA. Don't forget that you can download the table using the buttons at the upper left of the table.
Predicted sgRNA Binding Sites
Similar to the genomic binding sites, the predicted sgRNA binding sites tells you if the sgRNA has predicted target within an annotated gene or between two genes (intergenic). In case a sgRNA targets the same target more than once, the predicted target is only listed once.
Investigate Gene
Hit Confirmation Interaction Networks and Gene Set Enrichment
CRISPRAnalyzeR offers you the enrichment of gene sets with interaction networks from the String Database as well as additional information from EnrichR and various other databases.
Can I use several genes?
Yes, you can select single or multiple genes to start gene set analysis.
How is the Gene Set Analysis performed?
Gene Set Analysis is carried out using the Enrichr API available at the Enrichr website.
CRISPRAnalyzeR presents you each analysis with the Enrichr Combined Score, which is a combination of both the p-value and z-score:
c = log(p) * z
If you want to learn more about Enrichr, you can also check out the following publication:
Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, Duan Q, Wang Z, Meirelles GV, Clark NR, Ma'ayan A. Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;128(14) Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD, Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM, Lachmann A, McDermott MG, Monteiro CD, Gundersen GW, Ma'ayan A. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016; gkw377.
Pathways
CRISPRAnalyzeR checks the following databases for pathway information:
- WikiPathways 2016
- Wiki Pathway Database.
- KEGG 2016
- KEGG Database.
- Biocarta 2016
- Biocarta Database.
- Reactome 2016
- Reactome Database.
- NCI-Nature 2016
- NCI Nature Database.
- Panther 2016
- Panther Database.
Transcription
Gene Set Analysis is performed using different databases for transcriptional information provided by the Enrichr service
- ChEA 2015
- Enrichr Download Page.
- TRANSFAC and JASPAR PWMs
- JASPAR Transcription Factor Binding Sites.
- ENCODE and ChEA Consensus TFs from ChIP-X
- Download Dataset from Enrichr.
- TargetScan microRNA Targets
- TargetScan Website.
- Transcription Factor PPIs
- Download Dataset from Enrichr.
Ontologies
CRISPRAnalyzer uses Enrichr to get Gene Ontology Gene set analysis from the Gene Ontology Consortium.
- GO Biological Process 2015
- Gene Ontology Website.
- GO Cellular Component 2015
- Gene Ontology Website.
- GO Molecular Function 2015
- Gene Ontology Website.
Diseases
CRISPRAnalyzeR asks Enrichr to retrieve data from the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man® Database.
Cell Types
Retrieve genetic information about cell lines.
- Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia
- Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia.
- NCI-60 Cancer Cell Lines
- BioGPS Portal.
Protein Interactions
You can get a protein interaction network using the String Database.
- String Database
- String Database.
Select Genes
Select individual genes or gene lists
Select individual genes for Gene Set Analysis
Select gene lists for Gene Set Analysis
Hit Confirmation Gene Comparison
It is nice to know about possible hit candidates, but how about the sgRNAs?
This page provides you with a more in-depth view on the sgRNAs which you
used to target your favourite genes.
Compare the sgRNA populations of different genes using violin plots.
Find out more about violin plots at Wikipedia.
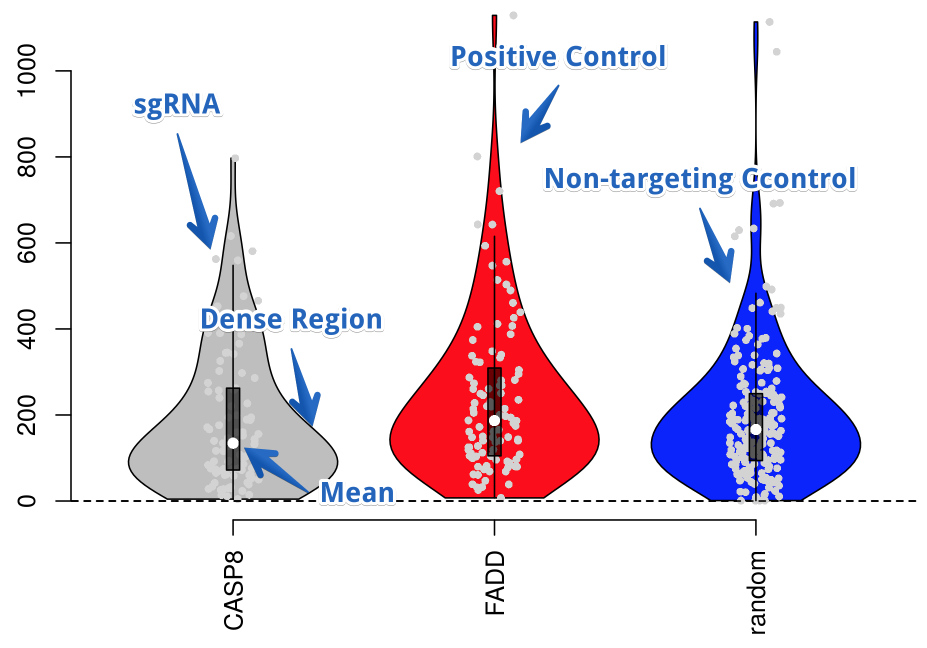
Readcount Untreated Group
This violin plots shows the normalized read counts of each sgRNA for the selected genes within the samples marked as the untreated group. The width of the violine gives you an impression of the sgRNA population density.
Readcount Treated Group
This violin plot shows the normalized read counts of all sgRNAs for the selected genes within the samples that have been set as part of the treated group.
Log2 Foldchange
Shows the log2-transformed fold change of all sgRNAs for the selected genes between your treated and untreated group.
Z-Score
Shows the z-score of sgRNAs for the selected genes.
sgRNA Binding Sites
Displays the number of predicted genomic binding sites of all sgRNAs for the selected genes. Genomic binding sites are predicted using E-CRISP.org with ignoring the first nucleotide and allowing up to two mismatches in total.
Compare Genes
Hit Confirmation Gene Annotation
The more information, especially about annotated fateures, you get about possible hit candidates - the better.
You can get annotation for multiple genes and compare these.
Select multiple genes as a variety of external information to annotate your genes of interest.
Selecting Genes
You can select multiple genes for which you would like to retrieve additional information. Just start typing the gene identifier and CRISPRAnalyzeR will show you the matching genes of your screen.
How many Annotations can I add?
CRISPRAnalyzeR allows you to enter up to 20 annotation features. Just start typing and CRISPRAnalzyeR will tell you which annotations match your input.
Which Annotations are available?
CRISPRAnalyzeR offers you all annotations available via the Ensembl biomaRt service
just start typing what you would like to know and CRISPRAnalyzeR will show you mathcing annotations directly. Moreover you will find a list of all available annotations below.
Which Genes do you wish to annotate?
Select (multiple) genes of interest.Available Annotations
Please select up to 20 different annotation features.The input supports instant search, so just type and find interesting annotations.
Download Report Adjust your report
CRISPRAnalyzeR not only provides you with individually plots and tables, but also gives you the opportunity to configure a report.
What is included in the report?
CRISPRAnalyzeR automatically includes all plots and data of the screen quality section and the hit calling section. For all additional information, you can specifically add those information by clicking on the 'Add to Report' button to tell CRISPRAnalyzeR that you would like to have this included in the report.
Tell CRISPRAnalyzeR which additional information should be added to the report
You can select which information is included in the report
The download page will tell you which information was be added to the report. Here you also have the chance to include or not include complete sections, which can be usefull if you would like to generate a report that only contains specific parts of the analysis.

Can I add additional information to the report?
In step2, you can add additional screening information and comments to the report, such as a screening title, the screening workflow procedure, a hypothesis, the used cell line and many more. We advise you to include as much information to have a complete documentation of the screen.
How can I download my report?
The report is generated once you click on the 'Create HTML Report' button at the bottom of the page. The report generation will take some time, dependend on the amount of included data and plots - please be patient. In the meantime you can use CRISPRAnalyzeR, as the report is generated in the background and will be downloaded to your device automatically.

You can get a full report including all data, which can be adjusted and downloaded on this site.
Once you created plots and tables on this website, you can also download them as part of an interactive HTML file. Thereby, you not only have them organized in a single document but they are also still interactive, which is good for browsing and exploring the data offline. If you really like our plots and want to use them for a presentation or print them, you can always click on the download icon in the top right corner of each plot - this also works in the downloaded report. By doing this, you can convert a plot to a .pdf, .png or other formats.
Step 1: Select Components that will be present in the report
In general, CRISPRAnalyzeR will add all common plots and tables to the report.
For all plots and tables that depent on your direct selection, you have to add these to the report by clicking a button.
Throughout CRISPRAnalyzeR you will find the 'Add to Report'-buttons, which will add the generated plots/tables to your report.
Please select the components to be included in your report:
|
|
Include plots and tables that represent your screen in various ways.
|
|---|---|
|
|
Include plots and tables of different differential expression analyses employed on your screen.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 2: Provide general information about your screen
A good reports needs additional information about the screening procedure.
Experiment Title
Aim / Hypothesis of the screen
Screening Procedure
Organism
Cell Line
Experimentator
Plasmid used
sgRNA Library Name
Number of Cells per sgRNA (Coverage)
Treatment
Sequencing Primer
Sequencing
Additional Comments
Please add further information in the text boxes above so CRISPRAnalyzeR can include them into your report.Help Ask us for help - send us a ticket
Our main goal was to keep CRISPRAnalyzeR easy-to-use and straight-forward.
We apologize for any inconvenience and aks you to please let us know what
struggled you.
Just send us a ticket with your
Name, Email-Adress and some description and we will get back to you
as soon as possible.
In the meantime you can join the Google Forum or read the FAQs.
Help Available Tutorials
Below you find tutorials on how to use CRISPRAnalyzeR or for specific settings you can adjust.
Available Video Tutorials
All tutorials can also be found on Youtube
CRISPRAnalyzeR Usage
How to upload FASTQ.gz data
How to find the right regular expression for FASTQ data
How to upload read count data
How to set the analysis parameters
Not available yet.How to assess the sequencing and screening quality
How to upload read count data and set the analysis parameters
How to find candidate genes in the Hit Calling section
Not available yet.How to annotate genes in the Hit Confirmation section
Not available yet.How to compare effects among multiple genes
Not available yet.How to set up and generate the interactive report
Not available yet.Installation
How to setup and install CRISPRAnalyzeR on macOS
Help Google Forum
Our main goal was to keep CRISPRAnalyzeR easy-to-use and straight-forward.
But - to be honest - with each new user things might come up that might
not be clear to the user or just don't work as intended.
We apologize for any inconvenience and ask you to please let us know what
struggled you.
To provide you a fast and convenient way of asking questions, please join
our Google Forum below.
Please have a look into the google groups of CRISPRAnalyzer for additional help. Check out the CRISPRAnalyzeR google group.
About CRISPRAnalyzeR About us / Imprint
This application is a non-commercial project, which is funded and hosted by the German Cancer Research Center (dkfz). It is developed by Jan Winter and Marc Schwering.

CRISPRAnalyzeR does not store personal information. All uploaded data is deleted immediately once the browser is closed or the connection is lost for any reason.
What data is stored?
CRISPRAnalyzeR does not store personal information. All uploaded data is deleted immediately once the browser is closed or the connection is lost for any reason.
CRISPRAnalyzeR only stores uploaded data for the time you visit the website.
Moreover, CRISPRAnalyzeR logs the following information
anonymously
for maintenance purposes:
Occuring error messages, file names, selected gene identifier, number of uploaded files, submit button activity and timestamps
CRISPRAnalyzeR uses the following technologies
Tools
| Version | |
|---|---|
| Bowtie2 | 2.29 |
| Highcharts | 5.04 |
| MAGeCK | 0.53 |
| R | 3.32 |
R Packages
Download CRISPRAnalyzeR Download the source code or a Docker container








